How GANs and AI-Generated Images Are Transforming Insurance Fraud Detection

Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and other advanced image-generation tools have revolutionized the digital landscape, empowering creators, developers, and businesses alike to achieve stunning visual realism. However, this technological leap has also introduced a serious challenge: increasingly sophisticated insurance fraud that is becoming harder than ever to detect.
GANs, at their core, use two neural networks working in opposition—a generator that creates realistic images and a discriminator that evaluates their authenticity. Through iterative competition, GANs learn to generate astonishingly realistic images and even videos, indistinguishable from real-world captures.
While GANs typically require significant technical skill to be utilized effectively, newer technologies such as ChatGPT’s 4o Image Generation tools are broadly accessible, meaning that anyone with access to a computer can easily produce realistic images, further complicating fraud detection efforts.
In the context of insurance, this technological prowess means that fraudulent claims could include fabricated images of vehicle damage, exaggerated property destruction, or falsified documentation that passes visual inspections with flying colors. Unlike traditional fraud, AI-generated visuals can seamlessly bypass human scrutiny, pushing fraud detection to new, challenging frontiers. Here are several concrete pitfalls and fraud scenarios insurers must watch for:
1. Fabricated Damage or Loss
Fraudsters can create entirely fake images of property, vehicles, or valuables showing damage or loss that never occurred. For example, a claimant might submit AI-generated photos of a car with collision damage or a home with water or fire damage, even though the incident never happened. E.g.:
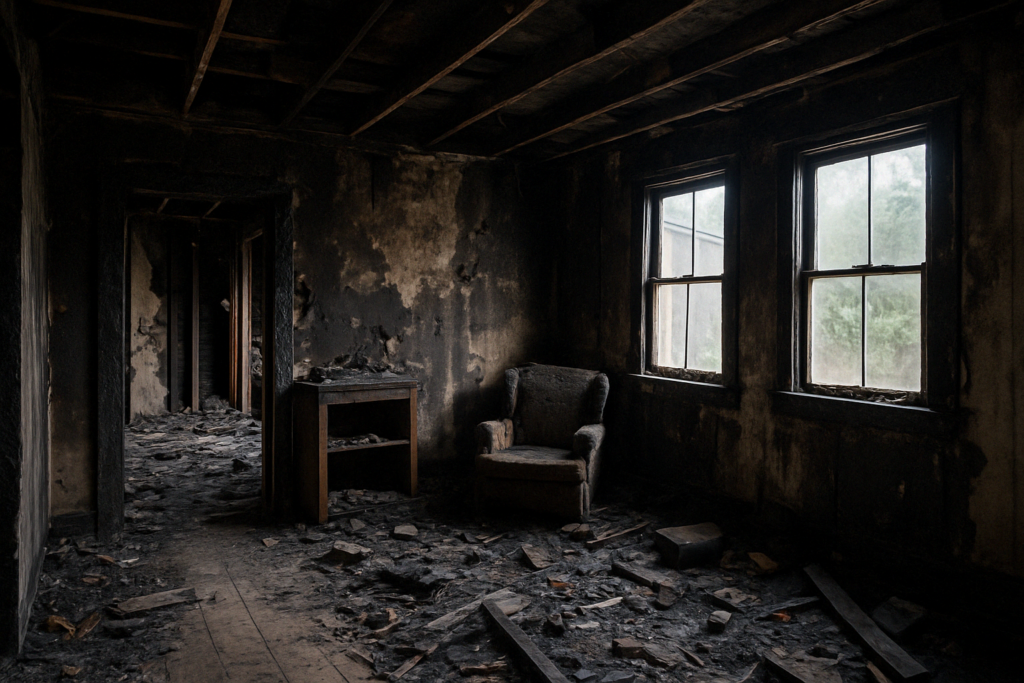

2. Exaggeration of Real Incidents
Real images can be manipulated to make actual damage appear much worse. For instance, a minor scratch on a vehicle can be digitally transformed into extensive body damage, or a small kitchen fire can be made to look like a total loss, inflating claim values.
3. Creation of Non-existent Insured Items
AI can generate convincing images of high-value items (e.g., jewelry, electronics, artwork) that never existed. Fraudsters may claim these items were lost, stolen, or destroyed, submitting fabricated images as proof.
4. Medical and Health Insurance Fraud
AI-generated x-rays or medical images could be used to support fraudulent health or disability claims. For example, a fake x-ray showing a bone fracture could be submitted to justify a claim for injury benefits. E.g.:
5. Manipulation of Incident Scenes
In liability or event insurance, AI can alter images to fabricate hazardous conditions or stage accidents. For example, a slip-and-fall claim might be supported by AI-edited photos showing a wet floor or missing safety signage that wasn’t present at the time.
6. Duplicate or Recycled Images
Fraudsters may use AI to slightly alter images found online or from previous claims, submitting them as new evidence for different claims or policies. This can be especially problematic in lines like cargo, marine, or fine art insurance, where unique items are involved.
7. Consistency Across Multiple Images
Advanced AI (such as GANs) can generate a series of images from different angles, all showing the same fabricated or exaggerated damage, making the fraud appear more credible and harder to detect.
8. Metadata Manipulation
AI tools can strip or falsify metadata (timestamps, geolocation, device info), making it difficult for insurers to verify when and where an image was taken, or whether it’s authentic.
9. Professional Liability and E&O Risks
If insurers or insured professionals rely on AI-generated images for underwriting, risk assessment, or claims decisions, errors or manipulations could lead to mispriced policies, inadequate coverage, or wrongful claim denials, exposing the insurer to liability.
10. Crop insurance
Fraudsters could use AI tools to generate images of crops allegedly damaged by hail, drought, pests, or other perils, when, in reality, no such damage occurred. E.g.:
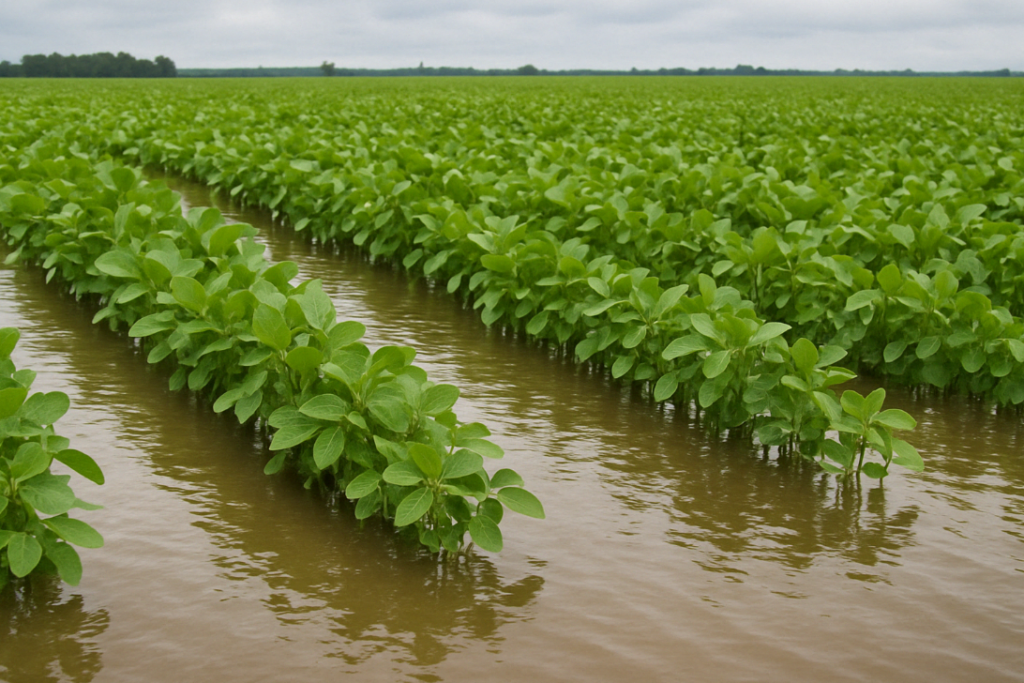

- Exaggerated Losses: Real images of minor crop issues may be manipulated to appear far more severe, inflating claim amounts.
- False Planting Claims: AI-generated or manipulated aerial images could be used to falsely document that crops were planted, or to misrepresent the type or extent of planted acreage.
- Yield Manipulation: Synthetic images may be created to support inflated yield loss claims, especially when visual evidence is required for indemnity.
To effectively mitigate the risks associated with AI-generated images, especially in the context of insurance claims and fraud detection, insurers should employ a multi-layered approach, beginning with basic verification techniques and progressing to advanced technological solutions.
These strategies include reverse image searches to detect reused or sourced images, metadata analysis to verify authenticity, employing dedicated external verification services that analyze digital fingerprints and cryptographic validation, and deploying AI and machine learning-based detection tools capable of flagging suspicious images rapidly.
Integrated forensic analysis further enhances these efforts by conducting comprehensive checks on images and documents, including digital fingerprinting and anomaly detection. Enhanced claim validation protocols, requiring multiple angles, timestamps, geotags, or live evidence, also strengthen fraud defenses.
Additionally, educating claims adjusters, special investigation units (SIUs), and other relevant personnel about the accessibility and potential misuse of these emerging image-generation technologies is critical to bolstering frontline fraud prevention efforts. Insurers must invest in continuous training, policy updates to mandate digital authenticity verification, and establish regular monitoring and feedback loops to adapt to evolving AI threats.
In conclusion, while GANs and sophisticated image-generation tools have opened doors to incredible digital creativity, they’ve also escalated the complexity of insurance fraud. Insurers must embrace equally sophisticated detection solutions, blending human intelligence with cutting-edge technology, to maintain trust and integrity in the age of AI.